| Fundamentals of Statistics contains material of various lectures and courses of H. Lohninger on statistics, data analysis and chemometrics......click here for more. |
|

Home  Bivariate Data Bivariate Data  Time Series Time Series  Filtering Signals Filtering Signals |
|
| See also: time and frequency, filtering in the frequency domain | |
Types of FiltersFiltering in its most general sense means removing parts of the spectrum of a signal. Depending on the part which is removed from the signal, there are several basic types of filters: 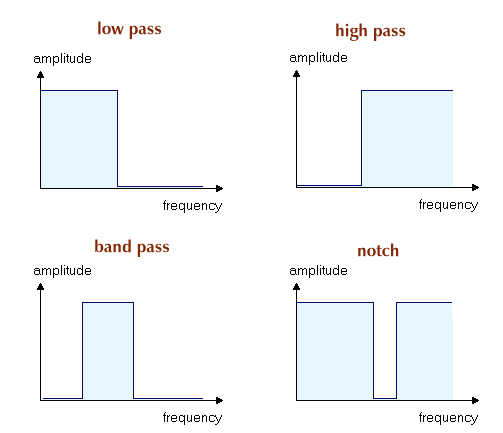 Low-pass filters cut off all high frequency parts of a signal, lower frequencies can pass the filter. Low-pass filters are closely related to smoothing procedures, such as moving averages. High-pass filters cut off the low parts of the spectrum and let the high frequencies pass. High-pass filters are related to the first derivative of a function. Band-pass filters are formed by a combination of low-pass and high-pass filters so that only frequencies within a certain range (band) can pass the filter. Notch filters remove a certain band from the frequency spectrum and are also formed by a combination of low- and high-pass filters. Please note that the characteristic frequency responses shown above are only theoretical curves - in reality the filter response functions do not show infinite steepness at the cutoff frequencies, nor do they exhibit a smooth transfer characteristic. Filter can be implemented both in analog and digital electronics. A few important digital filters are: The first two filter types are commonly known as state-space filter. |
|
Home  Bivariate Data Bivariate Data  Time Series Time Series  Filtering Signals Filtering Signals |
|

