| Fundamentals of Statistics contains material of various lectures and courses of H. Lohninger on statistics, data analysis and chemometrics......click here for more. |
|

Home  Statistical Tests Statistical Tests  Outlier Tests Outlier Tests  Nalimov-Test Nalimov-Test |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also: Outlier Tests | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nalimov TestAssuming a normal distribution of the sample the following simple test on outliers provides a quick hint (this test is also known as Nalimov test1, especially in German publications). A particular value x1 is considered to be an outlier if the statistic q
exceeds the critical threshold qcrit for a given level of significance. The number of degrees of freedom is defined as f= n-2 (table according to Kaiser/Gottschalk
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Home  Statistical Tests Statistical Tests  Outlier Tests Outlier Tests  Nalimov-Test Nalimov-Test |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


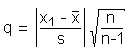
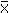 ....
....